Understanding Warranty Coverage
Source: cloudfront.net
Understanding car warranty terms and conditions – A car warranty is a promise from the manufacturer that certain parts of your vehicle will be repaired or replaced if they malfunction within a specified timeframe. Understanding the terms and conditions of your warranty is crucial for avoiding unexpected repair costs and ensuring your vehicle’s longevity. Different warranties offer varying levels of protection, and knowing what’s covered is vital for making informed decisions about vehicle maintenance and repairs.Warranty coverage protects you from costly repairs, but it’s not a blank check.
Each type of warranty has specific components and conditions that are essential to comprehend. Carefully reviewing the fine print in your warranty documents will help you identify the limits and exclusions of your coverage. This detailed understanding empowers you to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and potential repairs.
Different Types of Car Warranties
Various warranty types cater to different needs and circumstances. These include bumper-to-bumper, powertrain, and extended warranties, each with its unique coverage and exclusions.
Bumper-to-Bumper Warranty
This comprehensive warranty covers virtually all vehicle components from the front bumper to the rear bumper. It encompasses everything from the engine and transmission to the electrical system, interior components, and even the paint. However, there are typical exclusions. For instance, routine maintenance items like oil changes, tire replacements, and brake pad replacements are generally excluded. Also, damage caused by accidents, neglect, or modifications to the vehicle is usually not covered.
Powertrain Warranty
This warranty is focused on the core components of your vehicle’s powertrain. It typically covers the engine, transmission, and associated parts. This type of warranty often excludes components outside the powertrain, such as the electrical system, interior, or exterior. Specific exclusions regarding misuse, damage from accidents, or alterations to the vehicle’s mechanical components are usually detailed.
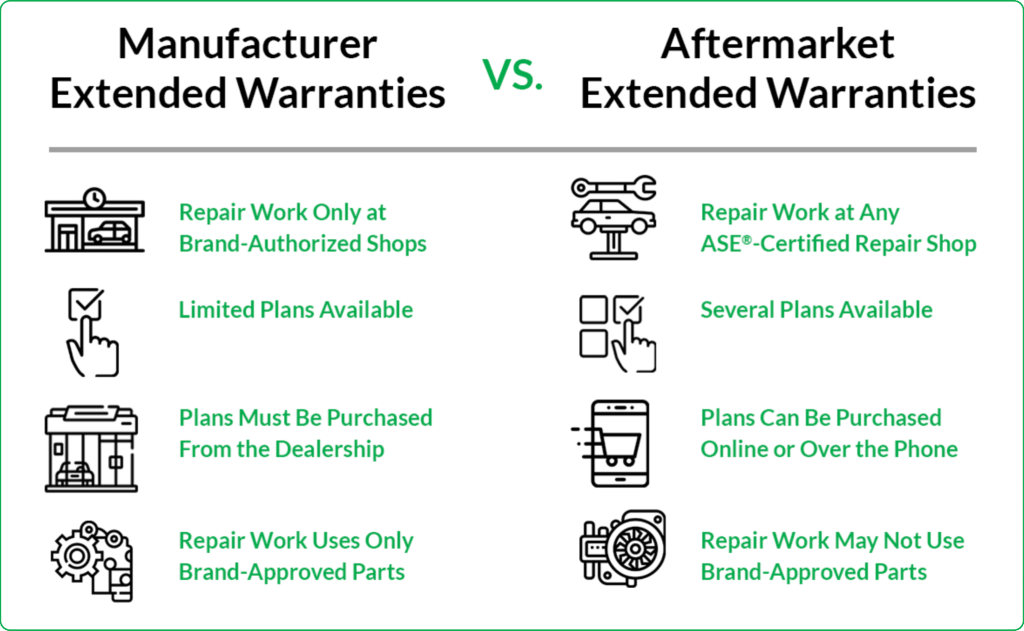
Extended Warranty
Extended warranties, often purchased after the initial manufacturer’s warranty expires, provide additional coverage for a specified period. These warranties can vary significantly in terms of the components covered and the exclusions. They frequently offer coverage for specific components beyond the scope of the initial manufacturer’s warranty. These warranties are usually more expensive than the initial manufacturer’s warranty and often have stringent terms and conditions that limit their applicability.
Warranty Coverage Comparison
| Warranty Type | Covered Components | Exclusions | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bumper-to-Bumper | Engine, transmission, electrical system, interior components, exterior components, etc. | Routine maintenance, accidents, neglect, modifications, wear and tear | Typically 3-5 years or 36,000-60,000 miles |
| Powertrain | Engine, transmission, and associated parts | Body parts, electrical system, interior components, routine maintenance, accidents, neglect, modifications | Typically 3-5 years or 36,000-60,000 miles |
| Extended | Varies greatly depending on the specific warranty | Varies greatly depending on the specific warranty, typically excludes routine maintenance, accidents, neglect, modifications, and wear and tear | Varies greatly depending on the specific warranty, typically several years |
Importance of Reading the Fine Print
Thorough examination of warranty documents is paramount to avoiding costly surprises. The fine print often contains crucial details regarding exclusions, limitations, and procedures for making claims. Understanding these details prevents disputes and ensures you’re fully aware of the extent of your coverage. It’s advisable to carefully read every line, paying particular attention to clauses related to maintenance, use, and potential damage.
Identifying Covered Repairs

Source: isure.ca
Understanding your car warranty involves more than just knowing what’s covered; it’s crucial to knowhow* to determine if a specific repair falls within that coverage. This section details the process for verifying warranty eligibility and highlights common scenarios where repairs might be included or excluded.Determining if a repair is covered requires careful review of the warranty document. The terms and conditions Artikel specific situations and components covered.
Look for explicit language regarding the type of repairs, parts, and circumstances under which the warranty applies. Pay attention to limitations and exclusions. This process often requires a detailed examination of the warranty’s specifics, including the scope of coverage, the timeframe for the warranty, and any associated limitations or exclusions.
Interpreting Warranty Terms
Warranty terms often use technical language. Understanding these terms is key to accurate interpretation. For example, the term “normal wear and tear” is often excluded. Likewise, repairs related to modifications or damage caused by accidents not covered by the warranty are often excluded. Accidents not related to the normal use of the vehicle are usually excluded.
The warranty document should clearly define these terms.
Common Repair Scenarios
To illustrate the practical application of warranty terms, consider the following table. This table represents common scenarios and their potential warranty status, based on typical warranty terms. Remember, actual coverage depends on the specific warranty details.
| Repair Scenario | Likely Covered? | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Engine failure due to a manufacturing defect within the warranty period | Likely Covered | Manufacturing defects are often covered under the warranty. |
| Replacement of a worn-out brake pad after 50,000 miles | Likely Excluded | Brake pads are considered wear items, typically excluded from coverage. |
| Damage to the car caused by a major accident (not a minor fender bender) | Likely Excluded | Accidents not covered by the warranty are typically excluded. |
| Replacement of the engine due to improper maintenance | Likely Excluded | Improper maintenance is typically not covered. |
| Repair of a cracked windshield due to a rock hitting it | Likely Excluded | Damage caused by external factors (like rocks) are often excluded. |
| Repair of a broken sunroof motor after 3 years | Potentially Covered (depending on warranty specifics) | Depending on the warranty specifics, a part’s lifespan can be covered for a certain period, or the specific repair might be included in the warranty. |
Understanding Warranty Limitations

Source: gotodobbs.com
Car warranties, while offering protection, come with limitations. Understanding these limitations is crucial to avoid disappointment when a repair is needed. These limitations are clearly Artikeld in the warranty document, but some common pitfalls are easily overlooked. Knowing these restrictions beforehand can help you make informed decisions about car maintenance and potential repairs.
Common Warranty Limitations, Understanding car warranty terms and conditions
Warranty coverage isn’t universal; it has specific exclusions. These limitations protect the manufacturer from claims stemming from factors outside their control or due to misuse. Knowing these exclusions helps you budget appropriately for repairs and avoid unnecessary disputes.
Wear and Tear
Normal wear and tear on parts of a vehicle is typically excluded from warranty coverage. This includes components that naturally degrade over time due to use, such as brake pads, tires, and upholstery. The warranty document usually defines what constitutes “normal” wear and tear, and this is often tied to mileage or time. For instance, a warranty might exclude replacement of brake pads after 50,000 miles of driving.
Misuse and Neglect
Warranty claims can be denied if the vehicle’s damage stems from misuse or neglect. This includes actions that deviate from the manufacturer’s recommended practices or improper maintenance. Examples of misuse include driving the vehicle aggressively, overloading it beyond its capacity, or using incorrect fuel types. Neglect, such as skipping regular maintenance, can also invalidate a claim.
Pre-Existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions, or problems present before the warranty period, are usually excluded. This means that if a part shows signs of failure or damage before the warranty starts, the manufacturer isn’t obligated to cover the repair during the warranty period. This exclusion often applies to issues that are detectable before the warranty commences.
Examples of Denied Claims
Warranty claims can be denied in several scenarios. For instance, if a vehicle is involved in an accident due to reckless driving, the damage caused by the accident likely wouldn’t be covered. Similarly, if a vehicle experiences damage due to improper fuel usage or a failure to perform routine maintenance, the repair may not be covered. Damage caused by aftermarket modifications can also be excluded.
Summary of Warranty Limitations
- Wear and Tear: Normal deterioration of parts due to regular use, such as brake pads, tires, and upholstery, is generally not covered. Warranty documents specify what constitutes normal wear and tear, often linked to mileage or time.
- Misuse: Damages arising from improper vehicle operation, like aggressive driving, overloading, or using incorrect fuel types, are not covered. Examples include accidents caused by reckless driving or damage due to improper fuel usage.
- Neglect: Failure to perform recommended maintenance, like ignoring scheduled services, can invalidate warranty claims. This includes situations where a lack of maintenance contributes to the failure of a component.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Issues present before the warranty period begins are typically not covered. This includes any problems detectable before the warranty commenced.
Navigating the Warranty Claim Process
Understanding your car’s warranty is crucial, but knowing how to navigate the claim process is equally important. A smooth and efficient claim process can save you time and frustration, ensuring a positive outcome. This section will detail the steps involved, emphasizing the importance of proper documentation and communication.
Steps in Filing a Warranty Claim
The warranty claim process generally involves several key steps. These steps, while potentially varying by manufacturer and dealership, usually follow a similar pattern. Understanding these steps will help you prepare effectively.
- Review Warranty Documents: Carefully examine your warranty policy. Identify the specific terms and conditions related to the covered repairs. Understanding the limitations and exclusions is critical before initiating the claim.
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Collect all relevant paperwork. This includes your vehicle’s purchase agreement, the warranty certificate, any repair orders from previous visits, and detailed descriptions of the current problem. Photos or videos of the damaged components can also be invaluable. Detailed notes of the problem, including when it first appeared and any specific conditions related to its occurrence, are crucial for a thorough claim.
- Contact the Dealership or Manufacturer: Reach out to the designated dealership or manufacturer to initiate the claim. Provide a clear and concise description of the problem. Be prepared to answer any questions they may have. Maintaining a polite and professional tone is key to a positive interaction.
- Provide Necessary Information: The dealership or manufacturer may require additional information, such as your vehicle identification number (VIN), the date of the problem’s occurrence, and the mileage of the vehicle. Be thorough and accurate in providing this information to avoid delays.
- Inspection and Evaluation: The dealership will inspect the vehicle to determine if the issue falls under warranty coverage. They will assess the damage and evaluate the repairs needed. Be prepared for questions about the vehicle’s history and maintenance records.
- Repair or Replacement: If the repair is covered under warranty, the dealership will perform the necessary repairs. If parts are replaced, ensure you receive confirmation of the parts used and that the work performed meets the warranty’s standards.
- Follow-up and Confirmation: After the repair, ask for a copy of the repair order confirming the work done. This serves as documentation for future reference.
Importance of Records and Documentation
Thorough documentation is paramount to a successful warranty claim. This helps to demonstrate that the issue falls under warranty coverage and aids in resolving any potential disputes. Keep all documents related to your vehicle, including repair records, maintenance logs, and warranty details, in a safe and organized manner. This allows you to quickly access necessary information when needed.
Clear and concise records of the issue’s progression, including dates and descriptions, will strengthen your claim.
Effective Communication with Dealerships or Manufacturers
Clear and professional communication with dealerships or manufacturers is essential for a smooth claim process. Be polite and respectful, but also firm in expressing your needs. Document all interactions, including the names of the individuals you speak with, the date and time of the conversations, and a summary of the discussed points. This documentation can prove invaluable if any issues arise during the claim process.
Avoid emotional language or aggressive behavior, and always remain focused on the facts.
Potential Timeframe for Processing a Claim
The timeframe for processing a warranty claim can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the issue, the availability of parts, and the manufacturer’s internal processes. Simple repairs might be resolved within a few days, while more extensive repairs or those involving parts shortages can take several weeks or even months. It’s essential to be patient and understanding, but also to follow up with the dealership or manufacturer regularly to check on the status of the claim.
Real-life examples include claims for engine repairs often taking longer due to part sourcing, while a simple light bulb replacement could be processed quickly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing a Warranty Claim
- Review Warranty Documents: Understand your coverage.
- Gather Documentation: Compile all relevant records, including purchase agreement, warranty certificate, repair orders, and photos/videos.
- Contact Dealership/Manufacturer: Initiate the claim, providing a clear description of the issue.
- Provide Necessary Information: Furnish the requested details, including VIN, date of problem, and mileage.
- Inspection and Evaluation: Allow the dealership to inspect the vehicle and determine coverage.
- Repair or Replacement: Confirm the repair and replacement parts used.
- Follow-up and Confirmation: Obtain a copy of the repair order and any necessary documentation.
Dispute Resolution
Warranty disputes, unfortunately, can arise when a customer believes their vehicle’s repair isn’t covered or when the repair process isn’t handled fairly. Effective resolution requires a structured approach, focusing on clear communication and documented evidence. Understanding the common causes, gathering crucial information, and exploring available resolution methods are key to navigating these situations successfully.A well-prepared case often leads to a positive outcome.
This involves meticulous record-keeping, clear communication with the dealership or manufacturer, and, if necessary, seeking help from consumer protection agencies. By following the steps Artikeld, consumers can confidently address warranty issues and obtain a favorable resolution.
Common Reasons for Warranty Disputes
Understanding the reasons behind warranty disputes is crucial for effective resolution. These issues often stem from misinterpretations of warranty terms, differing opinions on the cause of the vehicle problem, or disagreements on the scope of repairs covered. A breakdown of common causes includes:
- Incorrect Diagnosis: A mechanic might incorrectly diagnose a problem, leading to unnecessary repairs that aren’t covered under the warranty. This often arises from inadequate inspection or lack of expertise in the specific vehicle model.
- Disagreement on the Nature of the Defect: The manufacturer may disagree on whether a particular problem constitutes a defect covered by the warranty. The nature of the issue, its cause, and supporting evidence are critical to resolving this.
- Failure to Properly Document Repairs: Insufficient documentation of the problem’s existence before the repair can lead to disputes. Maintaining a detailed log of events, dates, and communications is vital.
- Disagreements on the Repair Cost: Repair costs can be a source of contention. A dispute may arise when the actual repair exceeds the manufacturer’s stated coverage or when the dealership charges an excessive amount.
Gathering Evidence and Documentation
Thorough documentation is essential for resolving warranty disputes effectively. This includes all communication, repair orders, receipts, and any other supporting evidence. A comprehensive record aids in proving the claim’s validity and strengthens the customer’s position.
- Maintain a Detailed Record: Document every communication with the dealership or manufacturer, including dates, times, and the names of individuals involved. Keep copies of all correspondence, repair orders, receipts, and estimates.
- Photographs and Videos: Photographs and videos of the damage or malfunctioning part can be powerful evidence, showcasing the issue’s existence before the repair.
- Expert Opinions: If needed, consider seeking expert opinions from independent mechanics or experts familiar with the vehicle’s make and model. Their assessments can add weight to the customer’s case.
- Warranty Documents: Ensure that the original warranty documents, including the terms and conditions, are readily available to support the claim.
Options for Resolving Warranty Disputes
Several avenues are available for resolving warranty disputes. These options range from informal negotiations to more formal complaints to consumer protection agencies.
- Negotiation: Attempting to resolve the dispute through direct negotiation with the dealership or manufacturer is often the first step. This may involve presenting the evidence gathered and seeking a mutually agreeable solution.
- Mediation: If direct negotiation fails, mediation can be an effective alternative. A neutral third party can help facilitate communication and find a resolution.
- Arbitration: Arbitration involves a neutral third party making a binding decision. This is often a quicker process than litigation, but it may involve specific fees.
- Litigation: Litigation, or a lawsuit, is a last resort. It’s a lengthy and costly process, but it may be necessary in cases where other options have been exhausted.
Examples of Successful Dispute Resolution Strategies
Successful strategies often involve a proactive approach, thorough documentation, and a willingness to explore all available options. One example involves a customer who meticulously documented every communication and repair attempt. This detailed record allowed them to successfully argue for a more comprehensive repair under warranty.
- Proactive Communication: Maintaining consistent and polite communication throughout the dispute resolution process is key. This includes keeping a record of all conversations and follow-up actions.
- Understanding Warranty Terms: A thorough understanding of the warranty’s specifics allows for a stronger case. Understanding the coverage, limitations, and the steps for filing a claim is critical.
- Gathering Comprehensive Evidence: Collecting and preserving all relevant documentation is crucial to supporting a claim. This includes repair orders, invoices, and correspondence.
Contacting Consumer Protection Agencies
Consumer protection agencies can be valuable resources in resolving warranty disputes. These agencies provide a platform for customers to file complaints and seek assistance in addressing issues with dealerships or manufacturers.
- Identify Relevant Agencies: Research consumer protection agencies at the state and national level. Their specific roles and responsibilities can vary.
- File a Complaint: Follow the agency’s guidelines for filing a complaint, providing all relevant details and supporting documentation.
- Seek Guidance: Contact the agency for guidance on navigating the complaint process and the available options.
Warranty Transfer and Sale: Understanding Car Warranty Terms And Conditions
Understanding how a car warranty transfers when a vehicle is sold is crucial for both the original buyer and the subsequent owner. This section details the conditions under which a warranty may be transferred, the responsibilities of each party, and the importance of proper documentation.Transferring a vehicle’s warranty can be complex, varying significantly based on the terms and conditions Artikeld in the original warranty agreement.
Not all warranties are transferable, and the specifics of any transfer must be meticulously followed to avoid disputes and ensure the new owner’s rights are protected.
Conditions for Warranty Transfer
The transferability of a car warranty hinges on the specific terms and conditions stipulated by the manufacturer or the seller. Generally, warranties are not automatically transferred upon a vehicle’s sale. Explicit clauses outlining the conditions for transfer must be present in the warranty document. The warranty might stipulate transferability only under certain circumstances, such as if the vehicle is sold to a certified mechanic or a dealer.
Examples include conditions that the vehicle’s mileage remains within a certain limit, or that the transfer is done within a specified time frame.
Role of the Original Buyer and New Owner
The original buyer plays a vital role in facilitating a smooth warranty transfer. They are responsible for ensuring the new owner is aware of the warranty’s status and any remaining coverage. This typically involves providing the new owner with a copy of the warranty document and any relevant supporting documents. The new owner, in turn, must adhere to the terms and conditions specified in the warranty document, ensuring that their use of the vehicle aligns with the warranty stipulations.
Importance of Documentation
Proper documentation is critical for proving the warranty transfer. This includes a copy of the original warranty, a sales contract that explicitly mentions the warranty transfer, and any communication confirming the transfer between the original and new owners. Detailed records of any maintenance performed on the vehicle are also valuable in case of future claims.
Warranty Transfer Process Flowchart
 This flowchart illustrates a typical warranty transfer process. It starts with the sale of the vehicle, then proceeds to the verification of warranty coverage, followed by the exchange of relevant documents, and concludes with the new owner being informed of the warranty details. Each step is critical in establishing a clear record of the transfer. Specific steps might vary depending on the warranty’s terms.
This flowchart illustrates a typical warranty transfer process. It starts with the sale of the vehicle, then proceeds to the verification of warranty coverage, followed by the exchange of relevant documents, and concludes with the new owner being informed of the warranty details. Each step is critical in establishing a clear record of the transfer. Specific steps might vary depending on the warranty’s terms.
Example of a Warranty Transfer Clause
“This warranty is transferable only if the vehicle is sold to a certified mechanic or an authorized dealer. The new owner must provide proof of purchase and the original warranty document to the dealership within 30 days of purchase. The original owner remains responsible for any claims related to the warranty period before the transfer.”


